Creating registries and devices
This page explains how to create, edit, and delete device registries and devices within them.
A device is a Thing in The Internet of Things. It is a processing unit capable of connecting to the internet (directly or indirectly) and exchanging data with the cloud. A device registry is a device container with shared properties. See Devices for more device and registry details.
If you still need to, complete the Getting started steps before proceeding.
Creating a device registry
To use ClearBlade IoT Core, you must create at least one device registry.
Console
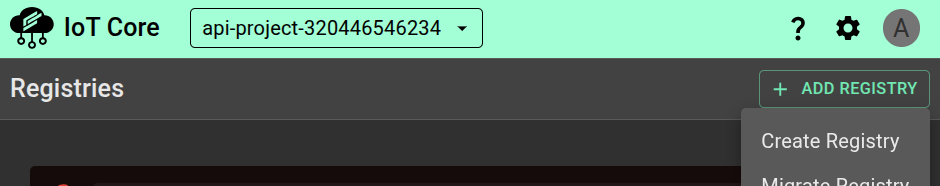
Go to the ClearBlade IoT Core console’s Registries page.
At the top of the page, click ADD REGISTRY, then select Create registry.
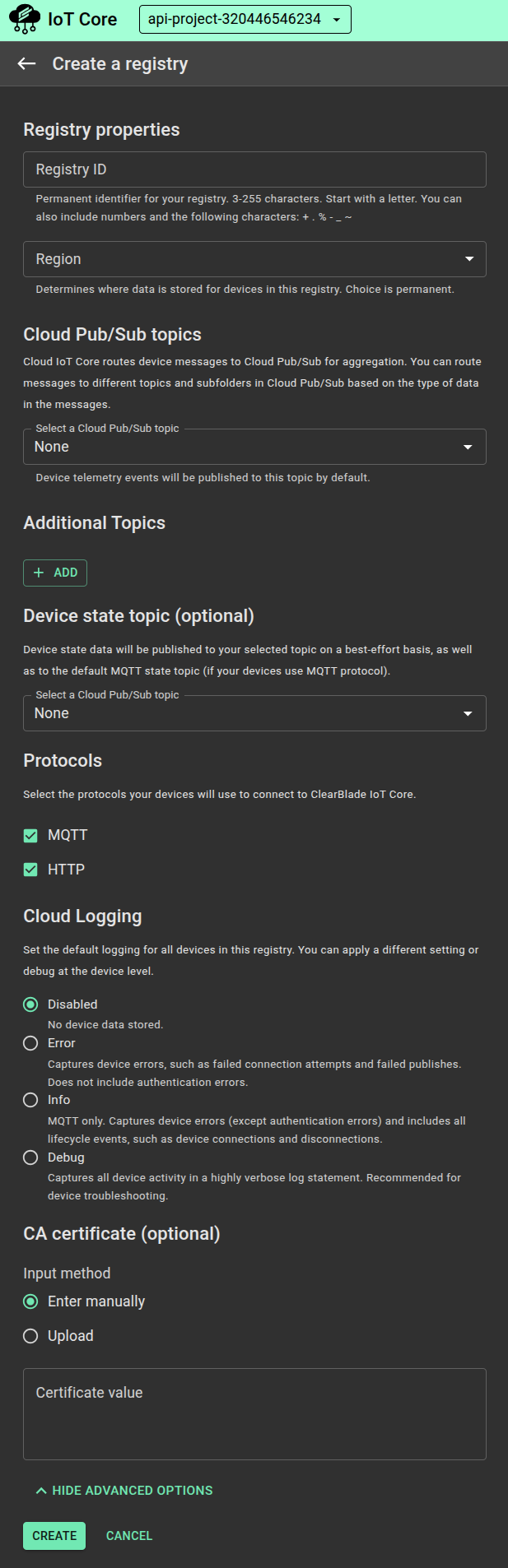
Enter a registry ID and select a cloud region. For registry naming and size requirements, see Permitted characters and size requirements.
Select the protocols that devices in this registry will use to connect to ClearBlade IoT Core: MQTT, HTTP, or both.
Use the Pub/Sub service to create new Pub/Sub topics.
Click CREATE to continue.
API
Creating a registry code samples
Use the DeviceRegistry create method to create a registry.
Node.js
// Client retrieved in callback
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
// Lookup the pubsub topic
const topicPath = `projects/${projectId}/topics/${pubsubTopicId}`;
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function createDeviceRegistry() {
// Construct request
const newParent = iotClient.locationPath(projectId, cloudRegion);
const deviceRegistry = {
eventNotificationConfigs: [
{
pubsubTopicName: topicPath
}
],
id: registryId
};
const request = {
parent: newParent,
deviceRegistry: deviceRegistry
};
const [response] = await iotClient.createDeviceRegistry(request);
console.log('Successfully created registry');
console.log(response);
}
createDeviceRegistry();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Create a registry");
string parent = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1";
string name = "Sample-New-Registry-2";
string pubsubTopic = "projects/developmentenv/topics/pubsubTopic";
RegistryConfigModel registryConfigModel = new RegistryConfigModel()
{
Id = name,
};
registryConfigModel.EventNotificationConfigs = new List<EventNotificationConfig>();
var toAdd = new EventNotificationConfig()
{
PubsubTopicName = pubsubTopic
};
registryConfigModel.EventNotificationConfigs.Add(toAdd);
var result = await mClient.CreateRegistry(4, parent, registryConfigModel);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to get a device states");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully obtained the list of device configuration versions");
// Use the obtained information
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def create_registry():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
pubsub_topic = 'your-pubsub-topic'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
parent = f"projects/{project_id}/locations/{cloud_region}"
if not pubsub_topic.startswith("projects/"):
pubsub_topic = "projects/{}/topics/{}".format(project_id, pubsub_topic)
registry = iot_v1.DeviceRegistry(
eventNotificationConfigs = [{ "pubsubTopicName": pubsub_topic }],
id = registry_id
)
request = iot_v1.CreateDeviceRegistryRequest(parent=parent, device_registry=registry)
try:
response = client.create_device_registry(
request=request
)
print("Created registry")
return response
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
create_registry()Go
package samples
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
iot "github.com/clearblade/go-iot"
)
// createRegistry creates a IoT Core device registry associated with a PubSub topic
func createRegistry(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, topicName string) (*iot.DeviceRegistry, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
registry := iot.DeviceRegistry{
Id: registryID,
EventNotificationConfigs: []*iot.EventNotificationConfig{
{
PubsubTopicName: topicName,
},
},
}
parent := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s", projectID, region)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Create(parent, ®istry).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Created registry:")
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tID: %s\n", response.Id)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tHTTP: %s\n", response.HttpConfig.HttpEnabledState)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tMQTT: %s\n", response.MqttConfig.MqttEnabledState)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tName: %s\n", response.Name)
return response, nil
}Creating device key pairs
Before creating a device, create a public/private key pair for it. When connecting to ClearBlade IoT Core, each device creates a JSON Web Token (JWT) signed with its private key, which ClearBlade IoT Core authenticates using the device's public key.
Creating or editing a device
Console
Go to the ClearBlade IoT Core console’s Registries page.
Click the device registry’s ID.
Click Devices in the left registry menu.
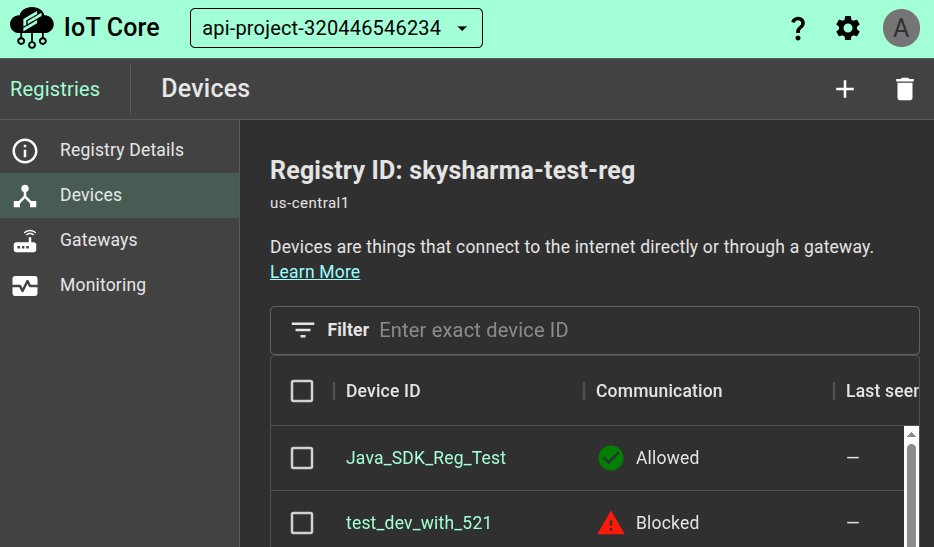
Click the '+' icon (top-right) to Create a device.
Enter a device ID that describes or identifies the device. This field cannot be edited later.
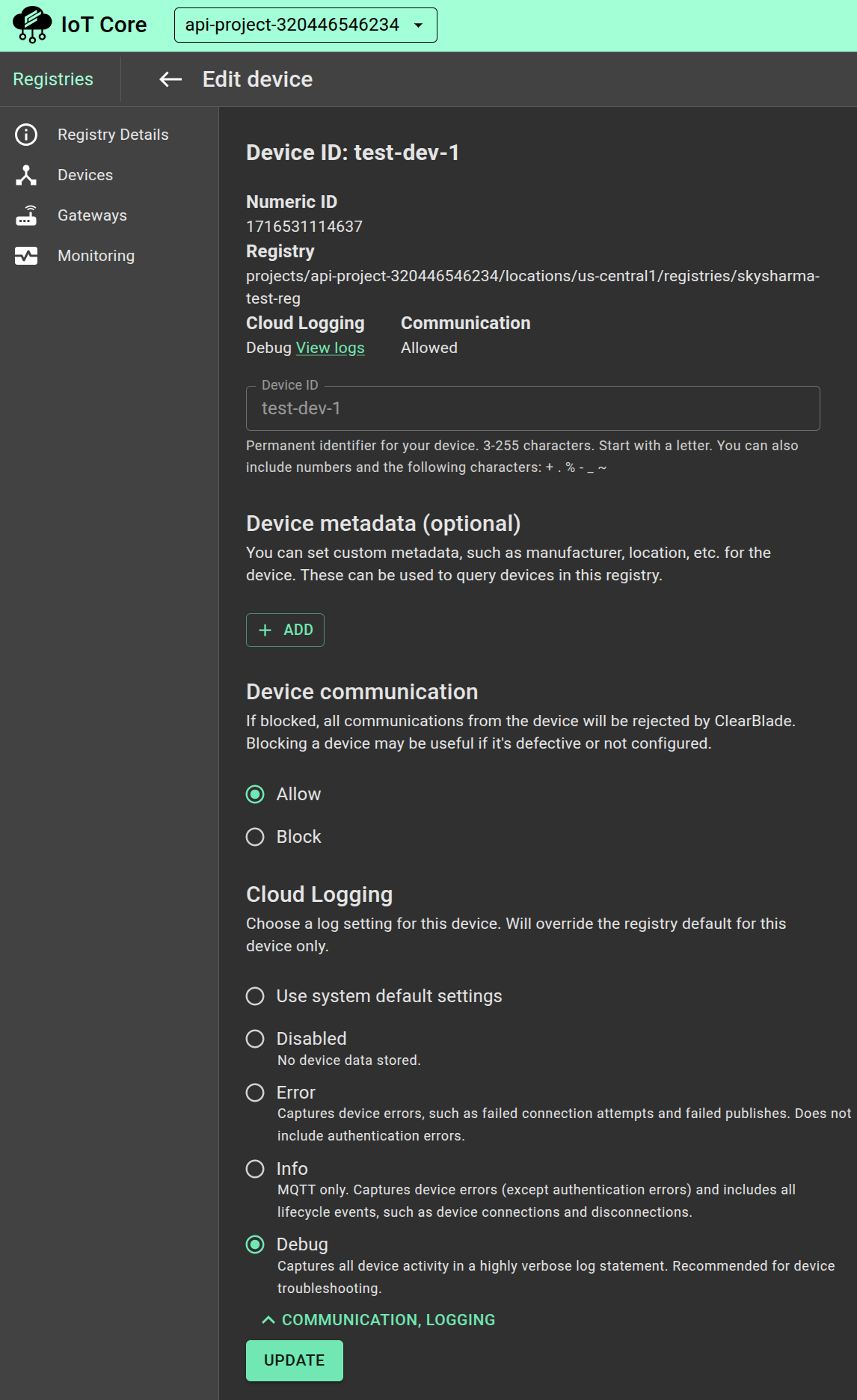
To edit an existing device, click its ID on the Devices page and click Edit device at the top of the page.
For Device communication, select Allow or Block. This option allows you to block communication when needed, such as when a device is not functioning properly. You'll most likely want to enable communication when creating the device.
If you're creating a new device, select the Input method you wish to use to enter the public key:
Manual: Copy and paste the public key into the Public key value field.
Upload: In the Public key value field, click Browse to select a file on your device.
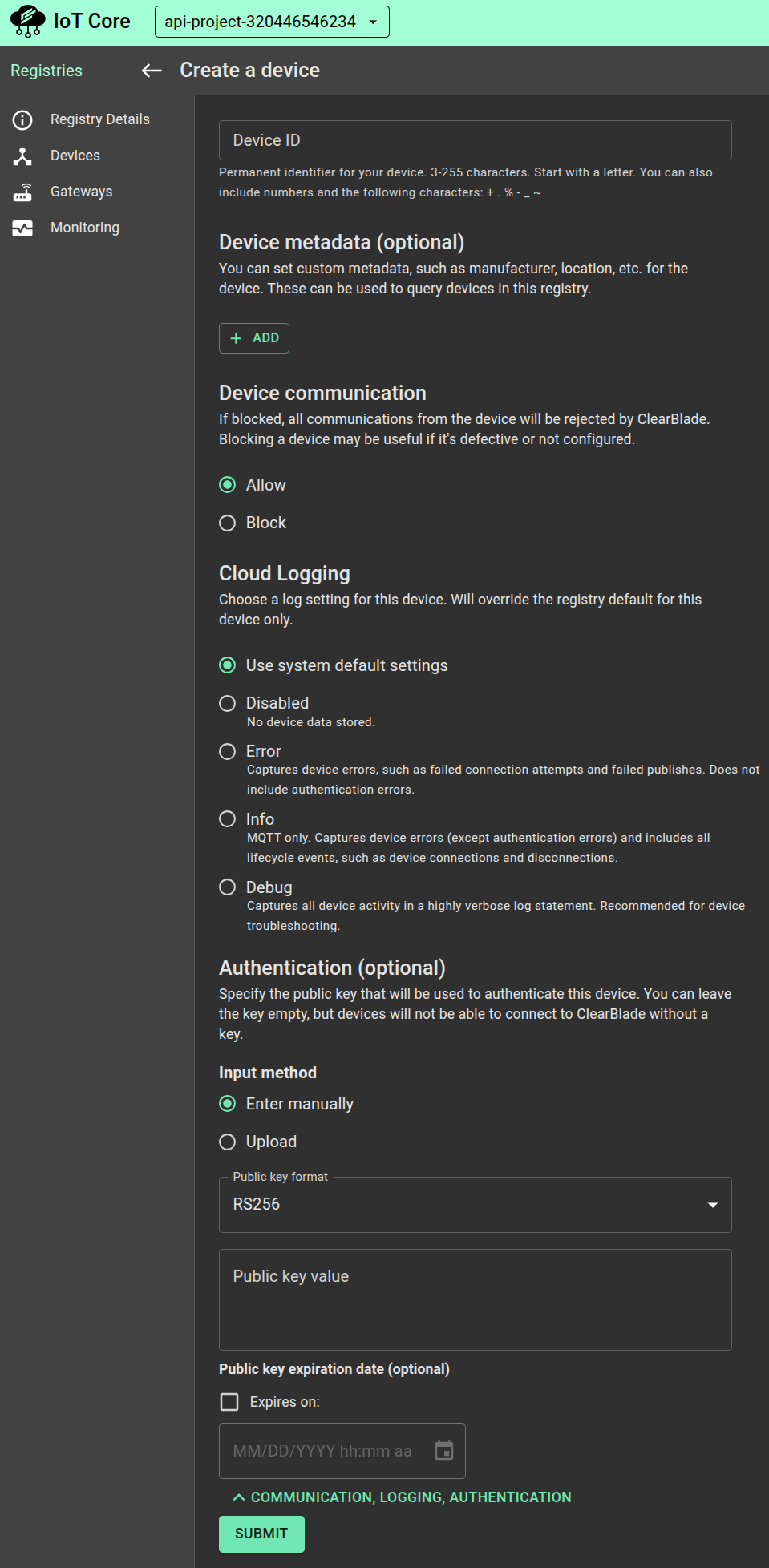
Select the public key format that matches this device’s key pair. Paste the certificate or key in the Public key value field. You can also set the key’s expiration date. To add a key to an existing device, click Add public key on the Device details page.
Use the Key and Value fields to add optional device metadata, such as a serial number.
Select a Cloud Logging level to determine which device events are sent to Cloud Logging.
Click Submit to create the device or Update to save changes to an existing device.
API
Use these methods to create or edit devices:
Public keys are specified in the Device resource’s credentials field in the ClearBlade IoT Core API when creating a device. You can add or modify this field when updating the device resource. If one or more registry-level certificates are present when adding a new device credential (via device creation or modifications), the public key credential must be signed by one of the registry-level certificates. See the device resource’s DeviceCredential for more information.
For RSA, theDevice.credentials[i].public_key.key field must be set to the rsa_cert.pem contents (including the header and the footer). The Device.credentials[i].public_key.format field must be set to RSA_PEM or RSA_X509_PEM.
For ES256, the Device.credentials[i].public_key.key field must be set to the ec_public.pem contents (including the header and the footer). The Device.credentials[i].public_key.format field must be set to ES256_PEM or ES256_X509_PEM.
Creating a device with RSA credentials code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-rsa-device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function createDevice() {
// Construct request
const regPath = iotClient.registryPath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId);
const device = {
id: deviceId,
credentials: [
{
publicKey: {
format: 'RSA_X509_PEM',
key: readFileSync(rsaCertificateFile).toString()
}
}
]
};
const request = {
parent: regPath,
device
};
const [response] = await iotClient.createDevice(request);
console.log('Created device', response);
}
createDevice();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Create a new device with RSA credentials");
string id = "Sample-New-Device";
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device";
String keyText = File.ReadAllText("path/to/key");
var credentials = new List<DeviceCredential>
{
new DeviceCredential()
{
PublicKey = new PublicKeyCredential()
{
Key = keyText,
Format = "RSA_X509_PEM"
},
}
};
var result = await mClient.CreateDevice(4, id, name, credentials);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to create new device");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully created new device");
// The result.Item2 object can be used to refer to newly created device
}
}Python
import os
import io
import json
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def create_device_with_rsa():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
certificate_file = 'path/to/certificate.pem'
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
parent = client.registry_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id)
with io.open(certificate_file) as f:
certificate = f.read()
# You can have multiple credentials associated with a device.
device = iot_v1.Device(
id = device_id,
credentials = [
{
"publicKey": {
"format": iot_v1.PublicKeyFormat.RSA_X509_PEM,
"key": certificate,
}
}
]
)
request = iot_v1.CreateDeviceRequest(parent=parent, device=device)
return client.create_device(request=request)
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
create_device_with_rsa()Go
// createRSA creates a device in a registry given RSA X.509 credentials.
func createRSA(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, deviceID string, keyPath string) (*iot.Device, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
keyBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(keyPath)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
device := iot.Device{
Id: deviceID,
Credentials: []*iot.DeviceCredential{
{
PublicKey: &iot.PublicKeyCredential{
Format: "RSA_X509_PEM",
Key: string(keyBytes),
},
},
},
}
parent := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s", projectID, region, registryID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.Create(parent, &device).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Successfully created RSA256 X.509 device: %s", deviceID)
return response, nil
}Creating a device with Elliptic Curve (EC) credentials code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-es-device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function createDevice() {
// Construct request
const regPath = iotClient.registryPath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId);
const device = {
id: deviceId,
credentials: [
{
publicKey: {
format: 'ES256_PEM',
key: readFileSync(esCertificateFile).toString()
}
}
]
};
const request = {
parent: regPath,
device
};
const [response] = await iotClient.createDevice(request);
console.log('Created device', response);
}
createDevice();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Create a new device with EC credentials");
string id = "Sample-New-Device";
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device";
String keyText = File.ReadAllText("path/to/key");
var credentials = new List<DeviceCredential>
{
new DeviceCredential()
{
PublicKey = new PublicKeyCredential()
{
Key = keyText,
Format = "ES256_PEM"
},
}
};
var result = await mClient.CreateDevice(4, id, name, credentials);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to create new device");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully created new device");
// The result.Item2 object can be used to refer to newly created device
}
}Python
import os
import io
import json
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def create_device_with_ec():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
public_key_file = 'path/to/ec_public.pem'
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
parent = client.registry_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id)
with io.open(public_key_file) as f:
public_key = f.read()
# You can have multiple credentials associated with a device.
device = iot_v1.Device(
name = device_id,
credentials = [
{
"publicKey": {
"format": iot_v1.PublicKeyFormat.ES256_PEM,
"key": public_key,
}
}
],
)
request = iot_v1.CreateDeviceRequest(parent=parent, device=device)
return client.create_device(request=request)
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
create_device_with_ec()Go
// createES creates a device in a registry with ES256 credentials.
func createES(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, deviceID string, keyPath string) (*iot.Device, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
keyBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(keyPath)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
device := iot.Device{
Id: deviceID,
Credentials: []*iot.DeviceCredential{
{
PublicKey: &iot.PublicKeyCredential{
Format: "ES256_PEM",
Key: string(keyBytes),
},
},
},
}
parent := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s", projectID, region, registryID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.Create(parent, &device).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Successfully created ES256 device: %s\n", deviceID)
return response, nil
}Patching a device with RSA credentials code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-rsa-device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function updateDevice() {
// Construct request
const devPath = iotClient.devicePath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId, deviceId);
const device = {
name: devPath,
credentials: [
{
publicKey: {
format: 'RSA_X509_PEM',
key: readFileSync(rsaPublicKeyFile).toString()
}
}
]
};
const [response] = await iotClient.updateDevice({
device: device,
updateMask: { paths: ['credentials'] }
});
console.log('Patched device:', deviceId);
console.log('Response', response);
}
updateDevice();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Update configuration of a device");
// While running this sample, it is assumed that, device with name
// "Sample-New-Device" exists
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/devices/Sample-New-Device";
var result = await mClient.GetDevice(4, name);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to get a device configuration");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully obtained the device configuration");
// Use the obtained information
string updateMask = "metadata";
string pubKey = "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA5P0Z4OUD5PSjri8xexGo\n6eQ39NGyQbXamIgWAwvnAs/oDRVqEejE2nwDhnpykaCGLkuDEN0LPd2wF+vC2Cq3\nY3YvkJh71IkjuAjMZQ+00CXdezfCjmTtEpMCNA3cV+G1g6uIcdEpHKs0YHfC9CFQ\nrjkc7tl3idmcQLngIov/gsFY7D1pbOgkCVVcZCRLgsdFfhCUYwYCvdEVJP3w+5mG\nybvmhNRbbFG7eG3+hmZoOg0h3f6r2fqgSx6l0+Z3D77SRT6lBEHvGDlxb08ASeuE\n0SJAc6PdAKd3FDqdZok4z1qJsgMqtU/ZGJJG54pNECWmhoOar+aQmmqnZ6kGQ5cn\nEwIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n";
result.Item2.Credentials.Add(new DeviceCredential
{
ExpirationTime = "",
PublicKey = new PublicKeyCredential
{
Format = "RSA_PEM",
Key = pubKey
}
});
result = await mClient.PatchDevice(4, name, updateMask, result.Item2);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to update a device configuration");
}
}Python
import os
import io
import json
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def patch_device_with_rsa():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
certificate_file = 'path/to/certificate.pem'
print("Patch device with RSA_X509 certificate")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
device_path = client.device_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id, device_id)
parent = client.registry_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id)
with io.open(certificate_file) as f:
certificate = f.read()
cred = {
"publicKey": {
"format": iot_v1.PublicKeyFormat.RSA_X509_PEM,
"key": certificate,
}
}
getDeviceRequest = iot_v1.GetDeviceRequest(
name=device_path
)
device = client.get_device(request=getDeviceRequest)
device.credentials.append(cred)
mask = "credentials"
updateDeviceRequest = iot_v1.UpdateDeviceRequest(
parent=parent,
device=device,
updateMask=mask
)
return client.update_device(request=updateDeviceRequest)
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
patch_device_with_rsa()Go
// patchDeviceRSA patches a device to use RSA256 X.509 credentials.
func patchDeviceRSA(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, deviceID string, keyPath string) (*iot.Device, error) {
// Authorize the client using Application Default Credentials.
// See https://g.co/dv/identity/protocols/application-default-credentials
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
keyBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(keyPath)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
device := iot.Device{
Id: deviceID,
Credentials: []*iot.DeviceCredential{
{
PublicKey: &iot.PublicKeyCredential{
Format: "RSA_X509_PEM",
Key: string(keyBytes),
},
},
},
}
parent := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s/devices/%s", projectID, region, registryID, deviceID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.
Patch(parent, &device).UpdateMask("credentials").Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Successfully patched device with RSA256 X.509 credentials")
return response, nil
}Credential and certificate expiration dates
When you create a device and add a public key, you can set the key’s expiration date. If the key was generated with a self-signed X.509 certificate, then the certificate has an expiration date. However, these two expiration dates are separate.
If the key or the self-signed X.509 certificate on the key expires, the device cannot connect to ClearBlade IoT Core. Additionally, if you try to create or update a device with an expired X.509 certificate, ClearBlade IoT Core returns an error.
Getting device details
Console
Go to the ClearBlade IoT Core console’s Registries page.
Click the device registry’s ID.
Click Devices in the left menu.
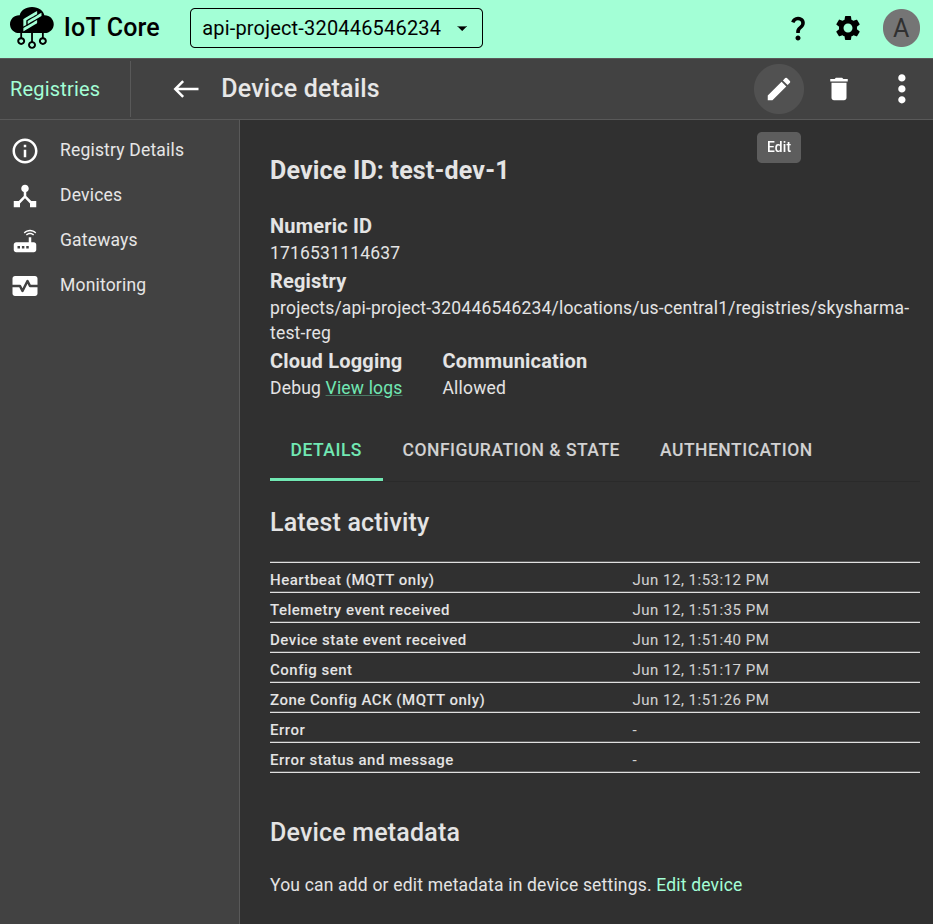
Click the device ID to go to the Device details page. This page summarizes recent device activity, including the last time a message was published and the most recent error time. This page also shows the device numeric ID.
Click the CONFIGURATION & STATE tab to see the device's recent configuration versions and update times.
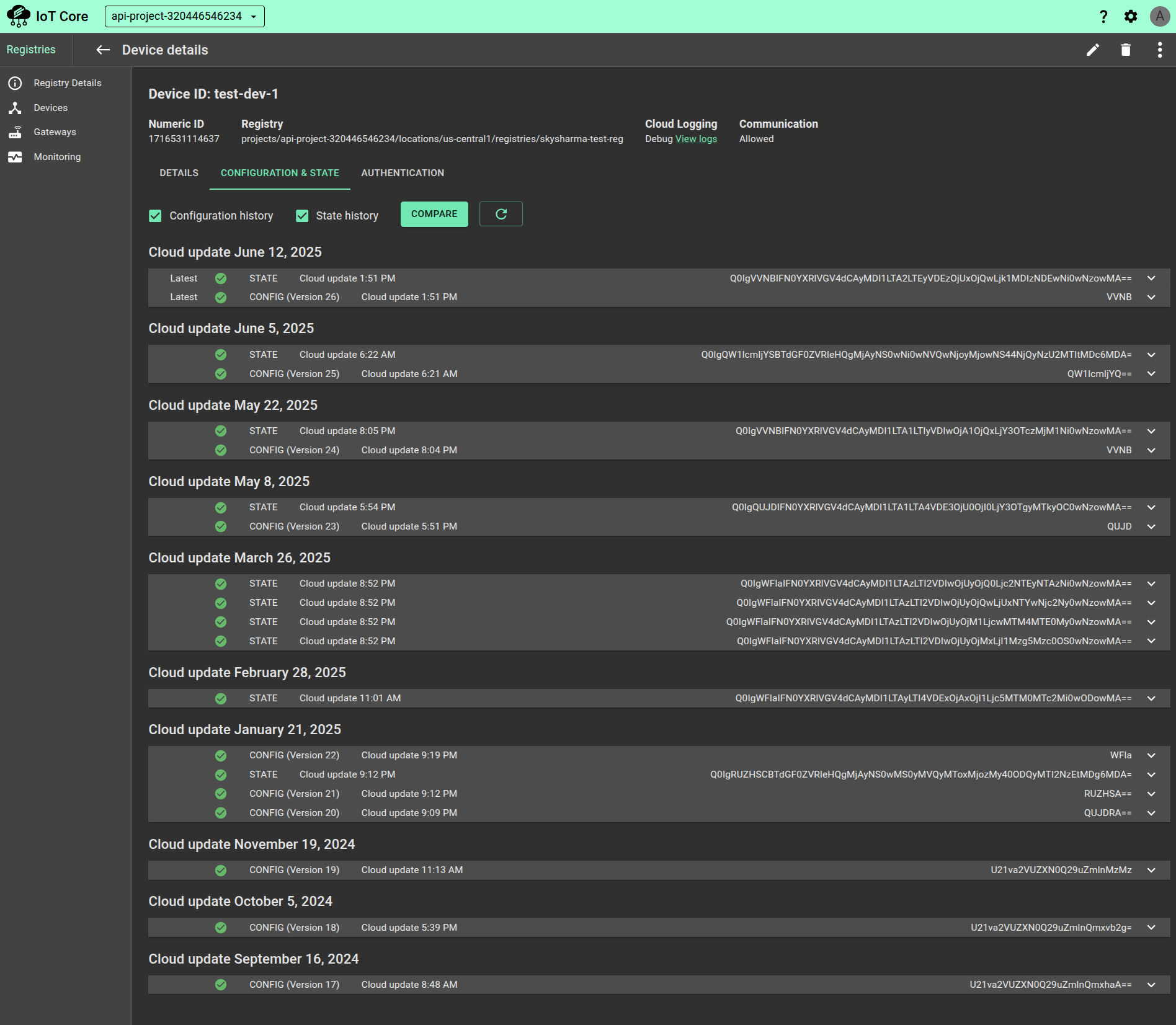
The fields for the last heartbeat time and the last time a configuration was ACKed are for the MQTT bridge only. The HTTP bridge does not support heartbeat or explicit ACKs.
API
Use these methods to get device details:
Device list method to list a registry’s devices
Device get method to get a device’s details
Device states.list method to list the device state’s last few versions in descending order
Listing the devices in a registry code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from "@clearblade/iot";
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function listDevices() {
// Construct request
const parentName = iotClient.registryPath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId);
// See the full list of device fields: https://clearblade.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/IC/pages/2207809724/projects.locations.registries.devices#Resource:-Device
const fieldMask = {
paths: [
"id",
"name",
"numId",
"credentials",
"lastHeartbeatTime",
"lastEventTime",
"lastStateTime",
"lastConfigAckTime",
"lastConfigSendTime",
"blocked",
"lastErrorTime",
"lastErrorStatus",
"config",
"state",
"logLevel",
"metadata",
"gatewayConfig",
],
};
const [response] = await iotClient.listDevices({
parent: parentName,
fieldMask,
});
const devices = response;
if (devices.length > 0) {
console.log("Current devices in registry:");
} else {
console.log("No devices in registry.");
}
for (let i = 0; i < devices.length; i++) {
const device = devices[i];
console.log(`Device ${i}: `, device);
}
}
listDevices();C#
if (bGetDevicesList)
{
logger.LogInformation("Obtain list of devices for a particular registry");
var result = await mClient.GetDevicesList(4, "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry");
if (!result.Item1)
logger.LogError("Failed to get list of devices");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Succeeded in getting the list of Devices");
// Use the list
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def list_devices():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
print("Listing devices")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
registry_path = client.registry_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id)
# See the full list of device fields: https://cloud.google.com/iot/docs/reference/cloudiot/rest/v1/projects.locations.registries.devices
# Warning! Use snake_case field names.
maskItems = [
"id",
"name",
"numId",
"credentials",
"lastHeartbeatTime",
"lastEventTime",
"lastStateTime",
"lastConfigAckTime",
"lastConfigSendTime",
"blocked",
"lastErrorTime",
"lastErrorStatus",
"config",
"state",
"logLevel",
"metadata",
"gatewayConfig",
]
field_mask = ','.join(maskItems)
request = iot_v1.ListDevicesRequest(
parent=registry_path,
fieldMask=field_mask
)
devices = list(
client.list_devices(request=request)
)
for device in devices:
print(device.id)
return devices
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
list_devices()Go
// listDevices gets the identifiers of devices for a specific registry.
func listDevices(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string) ([]*iot.Device, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
parent := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s", projectID, region, registryID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.List(parent).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Devices:")
for _, device := range response.Devices {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\t%s\n", device.Id)
}
return response.Devices, nil
}Retrieving a device and its metadata from a device registry code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from "@clearblade/iot";
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function getDevice() {
// Construct request
const devicePath = iotClient.devicePath(
projectId,
cloudRegion,
registryId,
deviceId
);
// See the full list of device fields: https://clearblade.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/IC/pages/2207809724/projects.locations.registries.devices#Resource:-Device
const fieldMask = {
paths: [
"id",
"name",
"numId",
"credentials",
"lastHeartbeatTime",
"lastEventTime",
"lastStateTime",
"lastConfigAckTime",
"lastConfigSendTime",
"blocked",
"lastErrorTime",
"lastErrorStatus",
"config",
"state",
"logLevel",
"metadata",
"gatewayConfig",
],
};
const [response] = await iotClient.getDevice({
name: devicePath,
fieldMask,
});
const data = response;
console.log("Found device:", deviceId, data);
}
getDevice();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Get configuration of a device");
// While running this sample, it is assumed that, device with name
// "Sample-New-Device" exists and version is updated to "2"
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device";
string localVersion = "2";
var result = await mClient.GetDeviceConfig(4, name, localVersion);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to get a device configuration");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully obtained the device configuration");
// Use the obtained information
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def get_device():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
print("Getting device")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
device_path = client.device_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id, device_id)
# See the full list of device fields: https://clearblade.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/IC/pages/2207809724/projects.locations.registries.devices
maskItems = [
"id",
"name",
"numId",
"credentials",
"lastHeartbeatTime",
"lastEventTime",
"lastStateTime",
"lastConfigAckTime",
"lastConfigSendTime",
"blocked",
"lastErrorTime",
"lastErrorStatus",
"config",
"state",
"logLevel",
"metadata",
"gatewayConfig",
]
field_mask = ','.join(maskItems)
request = iot_v1.GetDeviceRequest(
name=device_path
)
device = client.get_device(request=request)
print("Id : {}".format(device.id))
print("Name : {}".format(device.name))
print("Credentials:")
if device.credentials is not None:
for credential in device.credentials:
keyinfo = credential['publicKey']
print("\tcertificate: \n{}".format(keyinfo['key']))
print("\tformat : {}".format(keyinfo['format']))
print("\texpiration: {}".format(credential['expirationTime']))
print("Config:")
print("\tdata: {}".format(device.config.get('binaryData')))
print("\tversion: {}".format(device.config.get('version')))
print("\tcloudUpdateTime: {}".format(device.config.get('cloudUpdateTime')))
return device
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
get_device()Go
// getDevice retrieves a specific device and prints its details.
func getDevice(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, device string) (*iot.Device, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
path := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s/devices/%s", projectID, region, registryID, device)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.Get(path).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tId: %s\n", response.Id)
for _, credential := range response.Credentials {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\t\tCredential Expire: %s\n", credential.ExpirationTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\t\tCredential Type: %s\n", credential.PublicKey.Format)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "\t\t--------")
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tLast Config Ack: %s\n", response.LastConfigAckTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tLast Config Send: %s\n", response.LastConfigSendTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tLast Event Time: %s\n", response.LastEventTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tLast Heartbeat Time: %s\n", response.LastHeartbeatTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tLast State Time: %s\n", response.LastStateTime)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\tNumId: %d\n", response.NumId)
return response, nil
}Retrieving a device’s state from a device registry code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function listDeviceStates() {
const devicePath = iotClient.devicePath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId, deviceId);
const [response] = await iotClient.listDeviceStates({ name: devicePath });
const states = response.deviceStates;
if (states.length === 0) {
console.log(`No States for device: ${deviceId}`);
} else {
console.log(`States for device: ${deviceId}`);
}
for (let i = 0; i < states.length; i++) {
const state = states[i];
console.log('State:', state, '\nData:\n', state.binaryData.toString('utf8'));
}
}
listDeviceStates();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Get a device");
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device";
var result = await mClient.GetDevice(4, name);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to get a device");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully obtained the device");
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def list_device_states():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
device_path = client.device_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id, device_id)
getDeviceRequest = iot_v1.GetDeviceRequest(name=device_path)
device = client.get_device(request=getDeviceRequest)
print("Last state: {}".format(device.state))
print("State history")
listDeviceStatesRequest = iot_v1.ListDeviceStatesRequest(name=device_path)
states = client.list_device_states(request=listDeviceStatesRequest).device_states
for state in states:
print("State: {}".format(state.binary_data))
return states
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
list_device_states()Go
// getDeviceStates retrieves and lists device states.
func getDeviceStates(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, device string) ([]*iot.DeviceState, error) {
// Authorize the client using Application Default Credentials.
// See https://g.co/dv/identity/protocols/application-default-credentials
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
path := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s/devices/%s", projectID, region, registryID, device)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.States.List(path).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Successfully retrieved device states!")
for _, state := range response.DeviceStates {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s : %s\n", state.UpdateTime, state.BinaryData)
}
return response.DeviceStates, nil
}Deleting devices and registries
Console
Delete devices
1. Go to the ClearBlade IoT Core console’s Registries page.
2. Click the device registry’s ID.
3. Click Devices in the left menu.
4. Select each device you want to delete, then click Delete.
5. Confirm you want to delete the selected devices, then click Delete.
API
Use these methods to delete devices and registries:
Deleting a device from a registry code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function deleteDevice() {
// Construct request
const devPath = iotClient.devicePath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId, deviceId);
const [responses] = await iotClient.deleteDevice({ name: devPath });
console.log('Successfully deleted device', responses);
}
deleteDevice();C#
if (bDeleteDevice)
{
logger.LogInformation("Delete a device");
string id = "Sample-New-Device";
string name = "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device";
var result = await mClient.DeleteDevice(4, id, name);
if (!result.Item1 || (result.Item2 == null))
logger.LogError("Failed to delete device");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully deleted the device");
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def delete_device():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
print("Delete device")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
device_path = client.device_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id, device_id)
request = iot_v1.DeleteDeviceRequest(name=device_path)
return client.delete_device(request=request)
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
delete_device()Go
// deleteDevice deletes a device from a registry.
func deleteDevice(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, deviceID string) (*iot.Empty, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
path := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s/devices/%s", projectID, region, registryID, deviceID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.Delete(path).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Deleted device: %s\n", deviceID)
return response, nil
}Deleting a registry code samples
Node.js
// Client retrieved in callback
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function deleteDeviceRegistry() {
// Construct request
const registryName = iotClient.registryPath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId);
const [response] = await iotClient.deleteDeviceRegistry({
name: registryName
});
console.log(response);
console.log('Successfully deleted registry');
}
deleteDeviceRegistry();C#
{
logger.LogInformation("Delete a registry");
// While running this sample, it is assumed that, registry with name
// "Sample-New-Registry-2" exists
string name = "Sample-New-Registry-2";
var result = await mClient.DeleteRegistry(4, name);
if (!result)
logger.LogError("Failed to delete a registry");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully deleted a registry");
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def delete_registry():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
print("Delete registry")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
registry_path = client.registry_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id)
request = iot_v1.DeleteDeviceRegistryRequest(name=registry_path)
try:
client.delete_device_registry(request=request)
print("Deleted registry")
return "Registry deleted"
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
delete_registry()Go
// deleteDevice deletes a device from a registry.
func deleteRegistry(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string) (*iot.Empty, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
name := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s", projectID, region, registryID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Delete(name).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Deleted registry: %s\n", registryID)
return response, nil
}