Sending commands to devices
You can use ClearBlade IoT Core to send commands to devices. Commands are transitory, one-time directives sent to devices connected to ClearBlade IoT Core and subscribed to the commands topic.
Compared to device configurations, commands are faster, can be sent more frequently, and are independent of other ClearBlade IoT Core features. When choosing between commands and configurations, consider whether you need speed and time-bound directives (commands) or persistence/knowledge over time (configurations).
Commands can be useful when you want to:
Send messages quickly to many devices at a specific time
Send large-volume messages to many devices at a specific time
Send time-bound directives that should expire
Send incremental device settings
Commands have these characteristics:
Directly sent to subscribed, connected devices
Not persisted in ClearBlade IoT Core
Dropped for devices that are not subscribed and connected at the time the command is sent
Not unique (duplicates may be sent, though this is unlikely)
Not sent in any particular order (but delivered roughly in the send order)
In any format (data blob)
Currently, ClearBlade IoT Core supports commands over MQTT only (not HTTP).
Commands compared to configurations
ClearBlade IoT Core also supports device configurations. Configurations are more consistent and permanent than commands, and configurations persist in ClearBlade IoT Core. When using MQTT, the latest configuration is eventually delivered to all subscribed devices — even devices that subscribe later.
This table can help you decide whether to use a command or a configuration:
Configurations | Commands |
|---|---|
The latest config is retried until delivered (MQTT) | Retried for QoS 1, but not guaranteed to be delivered |
Persistent, so if a device connects (MQTT) or polls (HTTP) later, the most recent configuration will still be delivered | Not persistent; delivered only to devices connected at the time the command is sent |
Each new version replaces the previous version | No relationship or order among commands |
Tells a device what to be; corresponds to state in ClearBlade IoT Core | Tells a device what to do at a specific time |
Higher latency | Lower latency |
Typically small (max 64 KB) in size | Up to 256 KB |
Arbitrary, user-defined blob | Arbitrary, user-defined blob |
One update per sec per device | 1,000 per sec, per project (configurable) |
Because commands are not persisted in ClearBlade IoT Core and are not retried indefinitely, you should not expect device telemetry or state data to reflect a particular command. The device may not have received the command, or it may have received subsequent commands or configurations. Commands are intended to be transitory and are not part of long-term device data.
For QoS 1 subscriptions, an OK response indicates the device has received the command.
To manage command ordering and duplicates, use device logic or client applications.
Sending a command
Console
To send a command to a device:
Go to the ClearBlade IoT Core console’s Registries page.
Click the device registry ID.
In the left registry menu, select Devices.
Click the device ID you want to send the command.
At the top right of the page, click the ellipsis (⋮) and choose Send command.
Select the command’s format:
Text
Base64
In the Command data field, enter the command.
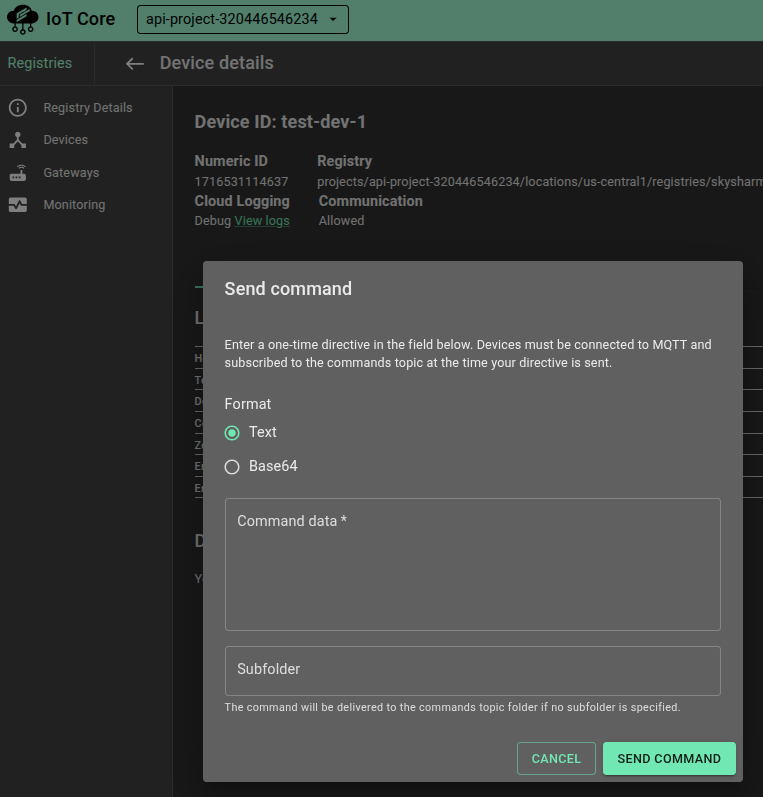
In the optional Subfolder field, enter the command’s Subfolder name. Devices that are subscribed to the wildcard topic will receive commands including those sent to Subfolders.
Click SEND COMMAND.
API
Use the SendCommandToDevice method to send a command.
Sending a command to a device code samples
Node.js
// const cloudRegion = 'us-central1';
// const deviceId = 'my-device';
// const commandMessage = 'message for device';
// const projectId = 'adjective-noun-123';
// const registryId = 'my-registry';
import { DeviceManagerClient } from '@clearblade/iot';
const iotClient = new DeviceManagerClient({
// optional auth parameters.
});
async function sendCommand() {
// Construct request
const formattedName = iotClient.devicePath(projectId, cloudRegion, registryId, deviceId);
const binaryData = Buffer.from(commandMessage);
const request = {
name: formattedName,
binaryData: binaryData
};
const [response] = await iotClient.sendCommandToDevice(request);
console.log('Sent command: ', response);
}
sendCommand();C#
if (bSendCommandToDevice)
{
logger.LogInformation("Send a Command to Device");
// Define the message you want to send
var data = new
{
binaryData = "QUJD"/*,
subfolder = "sub" - optional*/
};
var result = await mClient.SendCommandToDevice(4, "projects/developmentenv/locations/us-central1/registries/Sample-New-Registry/Devices/Sample-New-Device", data);
if (!result)
logger.LogError("Failed to send command to device");
else
{
logger.LogInformation("Successfully sent command to device");
}
}Python
import os
from clearblade.cloud import iot_v1
def send_command():
project_id = 'YOUR_PROJECT_ID'
cloud_region = 'us-central1'
registry_id = 'your-registry-id'
device_id = 'your-device-id'
print("Sending command to device")
client = iot_v1.DeviceManagerClient()
device_path = client.device_path(project_id, cloud_region, registry_id, device_id)
command = 'Hello IoT Core!'
data = command.encode("utf-8")
request = iot_v1.SendCommandToDeviceRequest(
name=device_path,
binary_data=data
)
return client.send_command_to_device(request=request)
os.environ["CLEARBLADE_CONFIGURATION"] = "/path/to/your-credentials.json"
send_command()Go
// sendCommand sends a command to a device listening for commands.
func sendCommand(w io.Writer, projectID string, region string, registryID string, deviceID string, sendData string) (*iot.SendCommandToDeviceResponse, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
service, err := iot.NewService(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req := iot.SendCommandToDeviceRequest{
BinaryData: b64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(sendData)),
}
name := fmt.Sprintf("projects/%s/locations/%s/registries/%s/devices/%s", projectID, region, registryID, deviceID)
response, err := service.Projects.Locations.Registries.Devices.SendCommandToDevice(name, &req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Sent command to device")
return response, nil
}Receiving a command
To receive a command, a device must:
Be connected to ClearBlade IoT Core using the MQTT protocol
Be subscribed to the MQTT topic
/devices/{device-id}/commands/#(the # wildcard is required)
By subscribing to the wildcard topic, the device will receive commands sent to devices/{device-id}/commands and subfolders (such as devices/{device-id}/commands/{subfolder}). Subscribing to a specific subfolder is not supported.
In most MQTT clients, the full topic (including the subfolder) is specified in the message received callback. This also applies to wildcard subscriptions.
Commands are delivered to connected and subscribed devices at that specific time. They are not queued or preserved for devices that connect and subscribe at a later time.
Quality of service (QoS)
Command delivery depends on the QoS level you're using:
QoS level | Guarantee |
|---|---|
0 | No guarantee (best effort only), even when the request returns |
1 | At-least-once delivery guaranteed if the sendCommandtoDevice request returns |
At QoS 0, a message is successful as soon as it is sent, regardless of the device’s response. At QoS 1, success means the device has acknowledged the message delivery. At-least-once delivery means the device may receive the command multiple times; ClearBlade IoT Core does not track how many times the command was received.
Errors
If the command timeout (60 sec, as noted in Quotas and limits) is reached,
DEADLINE_EXCEEDEDis returned.If the device is not connected or is connected but is not subscribed to the MQTT wildcard topic,
FAILED_PRECONDITIONis returned.
Logging
Commands sent to devices, as well as acknowledgments by devices, are logged in Cloud Logging.
Pricing
Commands are billed like all other messages sent over MQTT. For details, see Pricing.
