Streaming MQTT Connectors
ClearBlade’s streaming MQTT Connectors along for setting standard bi-directional mappings between data flowing over ClearBlade Brokered MQTT topics to Third party cloud streaming services and middleware.
This is ideal for sending MQTT messages into your cloud services or integrating data from other services directly with your ClearBlade application.
Currently supporting third party streaming offerings are
Google Pub/Sub - supports offline caching up to 10k messages
AWS Kinesis
Apache Kafka
Apache Pulsar
Azure Eventhub
Connect Collections
Technical Overview
To create a stream MQTT connect all that is required is to make a REST API call to the mqtt-connector endpoints and the system will immediately began honoring the configured mapping. ClearBlade recommends making this REST API call in a microservice that is triggered to run at IoT Enterprise environment start.
Environment Setup
Generally MQTT Connectors are designed to be started as the IoT Enterprise comes online and begins to allow device connections. When the service runs at start up it will make an HTTP call to the platform The recommended way to implement this is
Create a new Code Service of type micro-service
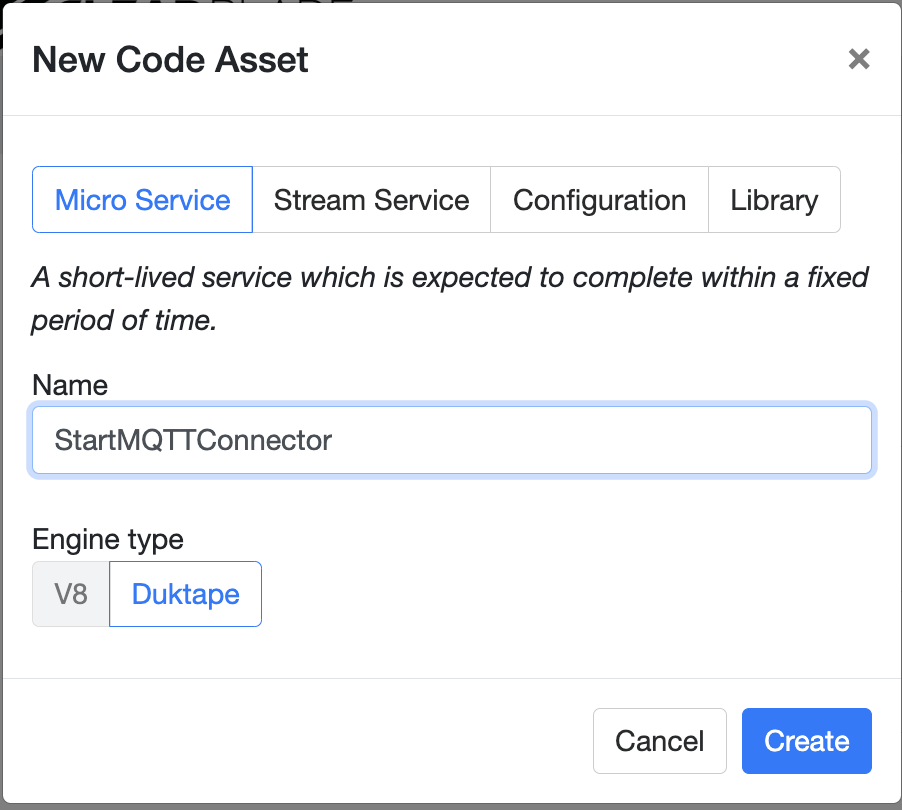
Include the http library
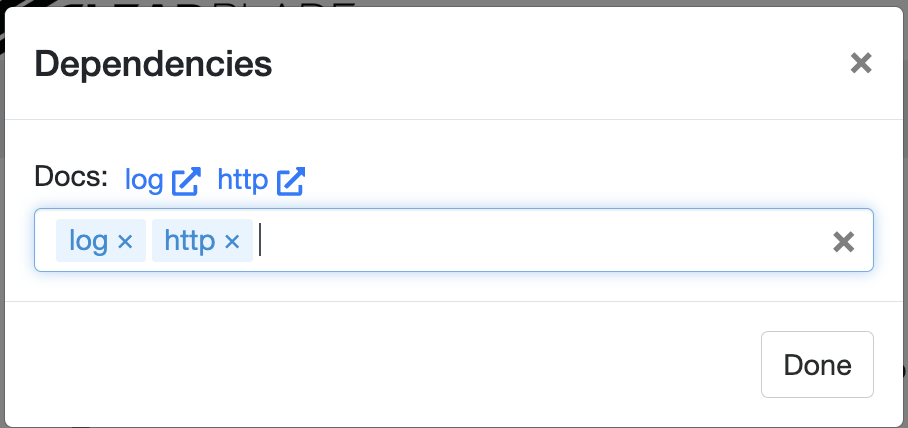
Click save
Next: Follow the connector setup. Use the sample code below and the appropriate configuration settings for your enterprise streaming binding.
When you are done click “Save and Test” to apply your mapping.

Connector Setup
The triggered micro-service will need to make an API call to the IoT Enterprise platform with the necessary configuration.
API:
Create
URI: /api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/{systemKey}/{name}
Method: POST
Headers: 'ClearBlade-UserToken': <userToken>
Body: { "type": <string>, "credentials": <object>, "config": <object> }
Update
URI: /api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/{systemKey}/{name}
Method: PUT
Headers: 'ClearBlade-UserToken': <userToken>
Body: { "type": <string>, "credentials": <object>, "config": <object> }
Get
URI: /api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/{systemKey}/{name}
Method: GET
Headers: 'ClearBlade-UserToken': <userToken>
Get All
URI: /api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/{systemKey}/
Method: GET
Headers: 'ClearBlade-UserToken': <userToken>
Delete
URI: /api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/{systemKey}/{name}
Method: DELETE
Headers: 'ClearBlade-UserToken': <userToken>
Sample Code
Ex: A sample micro-service to create a new MQTT Connector Configuration
function StartMQTTConnector(req, resp) {
const params = req.params;
const url = "https://"+cbmeta.platform_url+"/api/v/1/mqtt-connectors/"+req.systemKey+"/{name}";
const connectorConfig = {
"type": "google_pubsub", // pubsub, kinesis, kafka, pulsar
"credentials": {}, // specific to each type of connector
"config": {} // populate according to the connector
}
var options = {
"uri":url,
"body": connectorConfig,
"headers": {
"Content-Type" : "application/json",
'ClearBlade-UserToken': req.userToken
},
}
var requestObject = Requests();
// POST to create the MQTT connector
requestObject.post(options,function(err,body){
if(err){
//the error is a JSON value of the error in question, shaped like {"error":"message"}
resp.error("Failed to create MQTT Connector:" +err);
}else{
//body is JSON of the response
resp.success("Created MQTT Connector: "+body)
}
});
}Connector Configs
Google Pubsub
Added in 9.23.0
Credentials
"credentials": { // This is the service account JSON object
"project_id": "myprojectid",
"credentials_json":{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "myprojectid",
"private_key_id": "blahblahblah",
"private_key": "<priv_key>",
"client_email": "a@a.com",
"client_id": "9126871624161341",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/dahjkdhajkd%40dajsdgajdadsad.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
},Configuration
{
"topic_mappings": [
{
"pubsub_topic": "my-topic",
"outgoing": "foo/+/bar", //this topic will send to Google Pubsub
"sub_folder": ""
},
{
"pubsub_topic": "my-subscription",
"incoming": "foo/bar/baz", // this mqtt topic will receive from Google Pubsub
"sub_folder": "bob"
}
]
}
For Non IoT Core integrations, type is not used.
The following parameters exist for setting up your Google Pub/Sub forwarders to ClearBlade MQTT:
ack_strategy: 0 = ack immediately, 1 = never ack. For now, 0 should always be used.
poll_rate: Time (ms) between sending message batches to the broker. 0 will send messages immediately (deprecated after 9.36.x - ignored if included)
max_messages_per_poll: Max number of messages to send in a single batch to the broker. Implicit minimum value of 1 (deprecated after 9.36.x - ignored if included)
Messages are received by ClearBlade as soon as possible from Google. ClearBlade will buffer them internally and send them in batches as defined above.
AWS Kinesis
Added in 9.37.0
Credentials
{
"access_key": <string>,
"secret": <string>,
"region": <string>
}Configuration
{
"topic_mappings": {
<stream_name::string>: {
"outgoing": <outgoing_mqtt_topic::string>,
"incoming": <incoming_mqtt_topic::string>
}
},
"partition_key": <string>
}All fields required.
stream_name is kinesis stream name.
Data published on theoutgoing_mqtt_topic will be sent to the respective kinesis stream. This topic can have wildcards and it can be a shared topic.
Data received from the kinesis stream will be published on the incoming_mqtt_topic. This topic cannot contain wildcards or be a shared topic.
partition_key specifies the type of partition key used when putting records on the kinesis stream. The partition key has three types:
clientid: The MQTT client ID of the publisher will be used as the partition keytopic: The MQTT topic path will be used as the partition keyrandom: A randomly generated string will be used as the partition key
Apache Pulsar
Added in 9.39.1
Credentials
{
"url": <string>,
"tls_certificate": <string>,
"tls_key": <string>,
"tls_trusted_certificate": <string>
}url field is required, TLS fields are optional.
Configuration
{
"outgoing": [{
"pulsar_publish_topic": <string>,
"mqtt_subscribe_topic": <string>,
"key": <string>,
"ordering_key": <string>,
"hashing_scheme": <int>,
"compression_type": <int>,
"compression_level": <int>,
"router_type": <int>
}],
"incoming": [{
"pulsar_subscribe_topic_pattern": <string>,
"mqtt_publish_topic": <string>,
"subscription_name": <string>,
"subscription_type": <int>
}]
}Outgoing config options:
pulsar_publish_topic and mqtt_subscribe_topic fields are required.
hashing_scheme: 0 (default) = Java string hash, 1 = Murmur3 hash
compression_type: 0 (default) = no compression, 1 = LZ4, 2 = zlib, 3 = zstd
compression_level: 0 (default) = standard, 1 = faster, 2 = better
router_type: 0 (default) = round robin, 1 = single partition
Incoming config options:
pulsar_subscribe_topic_pattern, mqtt_publish_topic, and subscription_name are required.
subscription_type: 0 (default) = exclusive, 1 = shared, 2 = failover, 3 = key shared
! Note ! exclusive subscriptions will cause errors in clusters, as each cluster node will attempt to establish an exclusive subscription. Either shared or key shared is recommended in clusters.
Apache Kafka
Added in 9.39.1
Credentials
{
"seed_brokers": [<string>],
"tls": <bool>
"auth_mechanism": <string>,
"auth_params": <object>
},At least one seed broker url required. auth_mechanism required. If auth_mechanism != none, auth_params is required.
auth_mechanism can be one of: none, plain, oauth, aws, scram256, scram512.
auth_params:
plain: {
Zid: <string>, // optional authorization id
User: <string>,
Pass: <string>
}
oauth: {
Zid: <string>, // optional authorization id
Token: <string>,
Extensions: <object>
}
aws: {
AccessKey: <string>,
SecretKey: <string>,
SessionToken: <string>, // optional
UserAgent: <string> // optional
}
scram256/scram512: {
Zid: <string>, // optional authorization id
User: <string>,
Pass: <string>,
Nonce: <[byte]>, // optional
IsToken: <bool>, // set if user/pass are from a delegation token
}Configuration:
{
"topic_mappings": {
<string>: {
"incoming": <string>,
"outgoing": <string>
},
...
}
}The topic_mappings object keys are Kafka topic names. The incoming and outgoing fields are both MQTT topics. You must provide either an incoming or outgoing MQTT topic (or both) for every Kafka topic.
Azure Eventhub
Added in 2025.2.0
Credentials
{
"namespace_connection_string": <string>,
"eventhub_name": <string>,
"application_id": <string>
}namespace_connection_string is required
eventhub_name is only required if the connection string does not contain an entity path
application_id is optional
Configuration
{
"outgoing": [{
"mqtt_subscribe_topic": <string>,
"partition_key": <string>,
"partition_id": <string>
}],
"incoming": [{
"mqtt_publish_topic": <string>,
"consumer_group": <string>
}]
}Outgoing config options:
mqtt_subscribe_topic is required
partition_key and partition_id are optional. Only one of these values can be set at a time.
Incoming config options:
mqtt_publish_topic and consumer_group are required
The consumer group visibility is limited to a single system in a clearblade cluster. If two systems use the same consumer group, it will functionally behave as two separate consumer groups.
Collection Connector
Added in 2025.3.0
This connector can be used with any ClearBlade collection, including connect collections. The collection connector should be used with the batch connector to buffer write operations.
Credentials
Should be left empty
{}Configuration
{
"collection_id": "COLLECTION_ID",
"topics": ["YOUR", "TOPICS", "HERE"],
"payload_encoding": "utf8"
"column_mapping": {
"topic": "my_topic",
"payload": "my_payload",
"message_id": "mid",
"timestamp": "time",
"message_properties": {
"*": "properties"
"my_property": "my_property_column"
},
}
}Field Name | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | N/A | The ID of the collection to insert into. |
| Yes | N/A | The list of MQTT topics to subscribe to. Messages received are inserted into the collection. |
| No | utf8 | The method used to encode a MQTT publish body to a string. Options are “utf8”, “base64”, or “hex” |
| No | N/A | The name of the column in the collection to store the MQTT topic in. If left empty, the topic is not stored. |
| Yes | N/A | The name of the column in the collection to store the MQTT payload in. |
| No | N/A | The name of the column in the collection to store the MQTT message ID in. This will always be 0 for QoS 0 messages. If left empty, the message ID is not stored. |
| No | N/A | The name of the column in the collection to store the time at which the message was received by the broker. If left empty, the timestamp is not stored. |
| No |
| Maps a MQTT message property to the name of the column to store it in. See the table below for a list of all message properties |
Message Properties
The message_properties field is optional and allows you to map additional MQTT message properties to columns in your collection. Here’s a table with all the supported properties and their data types. Most correspond to the property by the same name in the MQTT spec:
Property Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
* | Blob | This is a special key that represents the entire MQTT message properties. It’s encoded according to the MQTT specification. |
payload_format_indicator | Int |
|
message_expiry_interval | Int | In seconds |
topic_alias | String |
|
content_type | String |
|
response_topic | String |
|
correlation_data | Blob |
|
Any keys in the message_properties object which do not match the names in this table are assumed to be MQTT 5 user property names.
Batch Connector
Added in 2025.3.0
The batch connector doesn’t publish to a third party service, but can be useful when used in conjunction with other connectors. It takes messages from one or more topics, aggregates them, then publishes them as batches onto a single topic.
This can be used to control the batching and buffering of messages when publishing to a third party API via another connector.
Credentials
Should be left empty
{}Configuration
{
"batch_options": {
"max_batch_size": 10,
"max_batch_delay_seconds": 5,
"batch_channel_size": 100
},
"topics": {
// Just an example
"my/device": "my/device/batch"
}
}Field Name | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 100 | The maximum number of MQTT messages to put in a single batch. Must be at least 1. |
| No | 10 | The maximum number of seconds that a message can be buffered while creating a batch. If this interval passes for the first message in a batch, then the entire batch is published, regardless of the batch size. |
| No | 1000 | The size of the internal buffer, in number of messages, that is used when creating batches. |
| Yes | N/A | The keys in this object are topics to subscribe to and batch. The value of a key is the topic to publish batches to. |
