Webhooks
A webhook is an interface that enables execution of a code service via a public endpoint. Webhooks can be assigned to:
Micro Services
Stream Services (by using the Preloader in the ClearBladeAsync code library)
Webhooks can be invoked using any HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH) all of which will result in the execution of the code service. The code service should be built to extract the method used during invocation and operate accordingly.
Webhooks support:
Header parameters
Query parameters
Multilevel paths
Wildcards in paths
Webhooks support these authentication methods:
ClearBlade
HTTP
Payload
No auth
Examples:
No auth micro service:
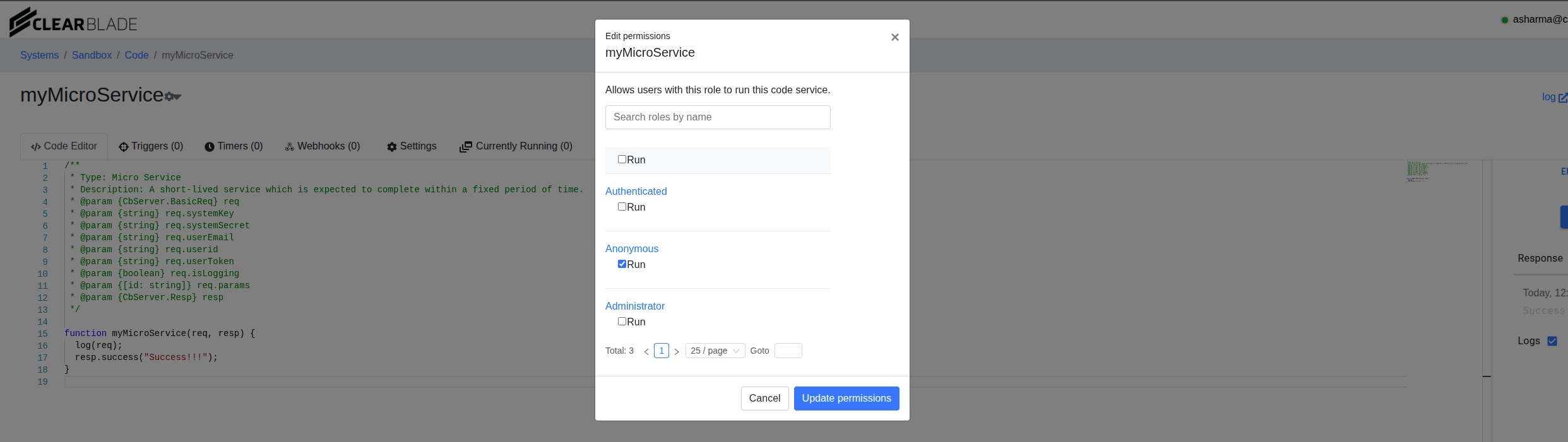
This simple micro service named myMicroService is set up to log the Request object - req. Looking at req in the code-logs will show how to extract these:
Method
Header parameters
Query parameters
Path
Note that in order to be a No auth webhook the Anonymous role should be allowed to execute the code service.
In the Webhooks tab…
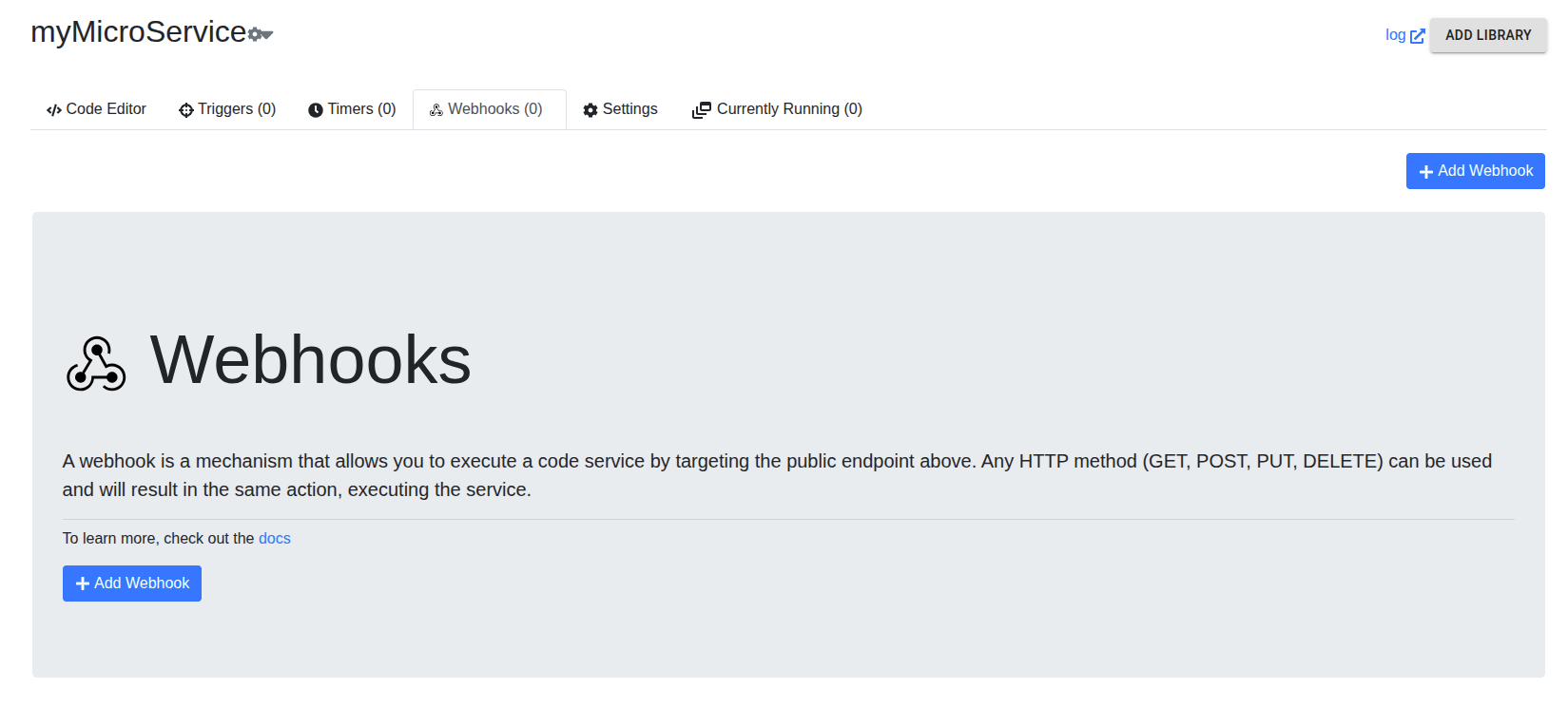
…we add a webhook. We give it a name, choose No auth for the Auth method, then click Create …
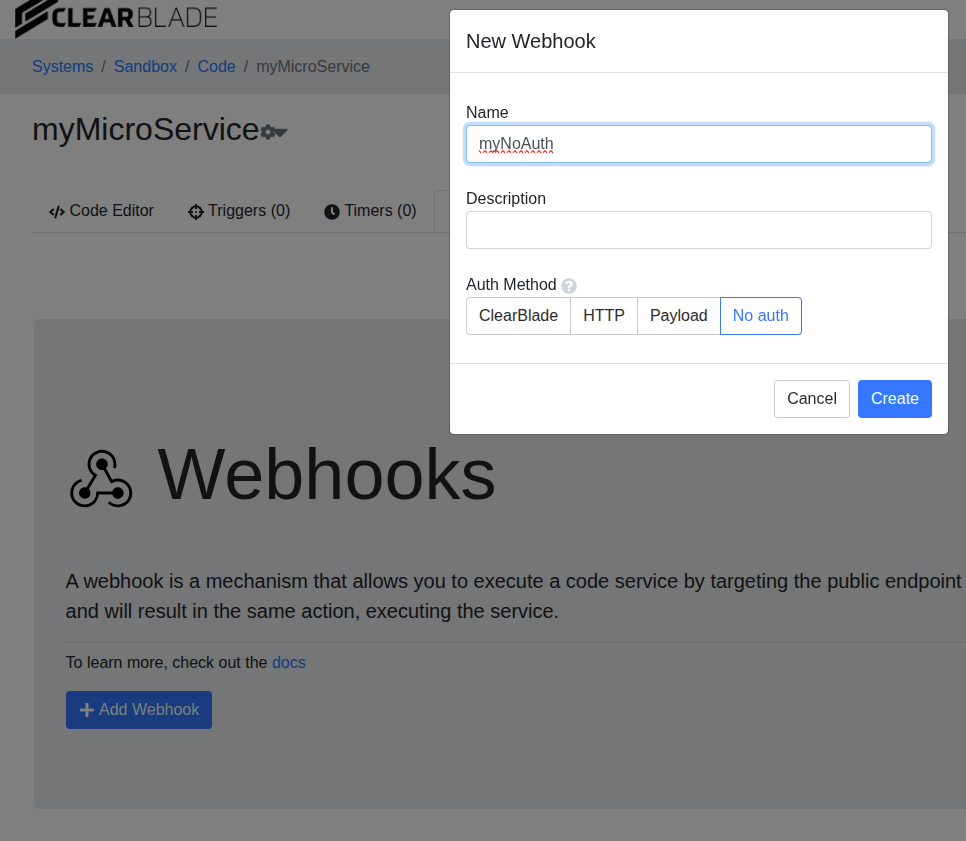
The webhook is created along with an endpoint we can copy.
The following shows the invocation of the webhook with the following:
Method: PUT
Header parameters:
MyHeader1=ABC
YourHeader2=DEF
Query parameters:
MyQueryParam=[“dog”, “cat”, “fish”]
YourQueryParam=”cow”
Path: subDir/subSubFolder
CODEcurl -X PUT -H "MyHeader1: ABC" -H "YourHeader2: DEF" "https://your.url.com/api/v/4/webhook/execute/yourSystemKey/myNoAuth/subDir/subSubFolder?MyQueryParam=dog&MyQueryParam=cat&MyQueryParam=fish&YourQueryParam=cow"
Looking at the code-log captured…
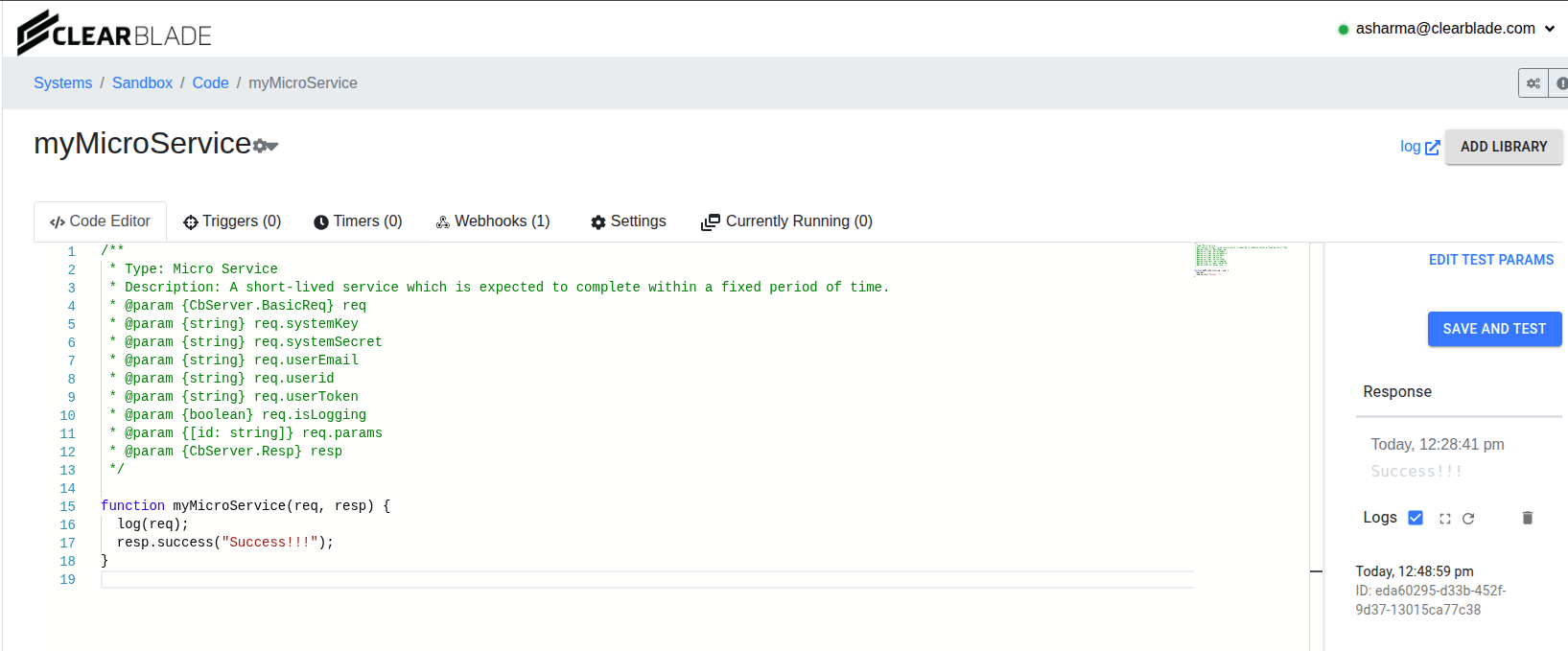
…we see the following:
{
"params": {
"body": {},
"query": {
"MyQueryParam": [
"dog",
"cat",
"fish"
],
"YourQueryParam": [
"cow"
]
},
"headers": {
"User-Agent": [
"curl/8.5.0"
],
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"Myheader1": [
"ABC"
],
"Yourheader2": [
"DEF"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"123.123.123.123"
],
"Connection": [
"close"
]
},
"urlParams": {},
"method": "PUT",
"uri": "/api/v/4/webhook/execute/yourSystemKey/myNoAuth/subDir/subSubFolder"
},
"systemKey": "yourSystemKey",
"userToken": "yourUserToken",
"isLogging": true,
"userid": "anon",
"userEmail": "anon",
"service_instance_id": "1234-1234-1234-1234",
"caller": {
"userid": "anon",
"userEmail": "anon",
"userToken": "yourUserToken"
}
}
The method, headers, query parameters and path can be extracted from the req object.
NOTE: No Anon token is required to invoke this webhook.
Micro service with ClearBlade auth:
If we change the Auth method to ClearBlade…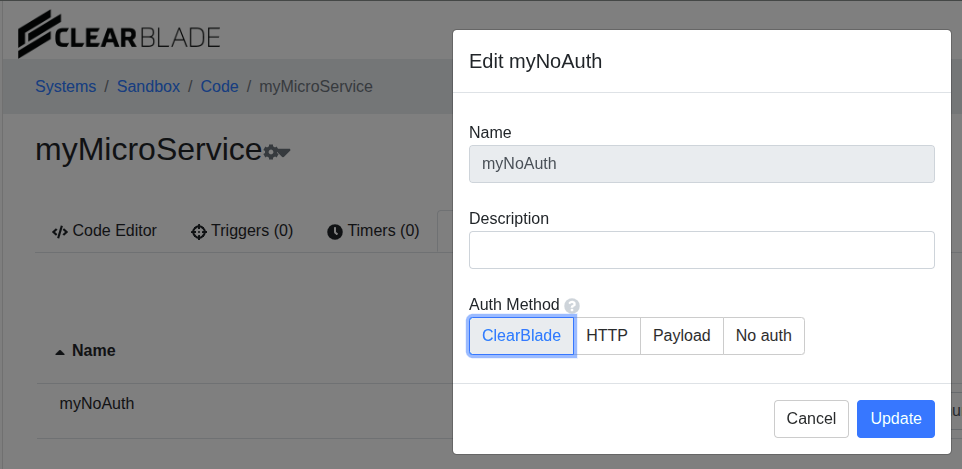
…we must include a ClearBlade-UserToken header in the request…CODEcurl -X PUT -H 'ClearBlade-UserToken: myUserToken' -H "MyHeader1: ABC" -H "YourHeader2: DEF" "https://your.url.com/api/v/4/webhook/execute/yourSystemKey/myNoAuth/subDir/subSubFolder?MyQueryParam=dog&MyQueryParam=cat&MyQueryParam=fish&YourQueryParam=cow"…to have the code service execute successfully.
Here ClearBlade-UserToken is either the cb_token for a Service Account User or Device, OR it is a token obtained with a POST request to one of these:/api/v/2/devices/{SystemKey}/auth/api/v/1/user/auth
Path Wildcards
The ClearBlade Developer Console does not allow you to specify a path when creating or updating a Webhooks. The admin/v/4/webhook REST API must be used to specify a path.
Wildcards can be inserted into the path of a Webhook. Wildcards can be used as an alternative method to pass dynamic data into a Webhook. Wildcards are specified by placing “{}” around an entire path element. The path element should resemble a typical placeholder/variable name. When a request to the Webhook is received, the placeholders will be parsed from the URI of the Webhook and placed in the params.urlParams object of the incoming request.
Example:
If you were writing a code service that returned all devices located in a specific US state for a specific device type, your path may look like the following:
/states/{stateCode}/devices/{deviceType}When using the admin/v/4/webhook REST API, the body will be a JSON object with the following structure:
{
"auth_method": "[AUTH_METHOD]",
"description": "",
"name": "[WEBHOOK_NAME]",
"service_name": "[CODE_SERVICE_NAME]",
"path": "[PATH_WITH_OR_WITHOUT_WILDCARDS]"
}Example:
Using the all devices located in a specific US state for a specific device type example above, the JSON used to create the Webhook would resemble the following:
{
"auth_method": "no_auth",
"description": "Find devices of a specific type located in a specific US state",
"name": "findDevicesInStateWebhook",
"service_name": "findDevicesInState",
"path": "/states/{stateCode}/devices/{deviceType}"
}The Webhook could then be invoked with a url resembling
https://myInstance.clearblade.com/api/v/4/webhook/execute/[YOUR_SYSTEM_KEY]/findDevicesInStateWebhook/states/TX/devices/tractorThe resulting request received by the code service would resemble:
{
"caller": {
"userEmail": "anon",
"userToken": "...",
"userid": "anon"
},
"isLogging": true,
"params": {
"body": "",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"Accept-Encoding": [
"gzip, deflate, br"
],
"Cache-Control": [
"no-cache"
],
....
},
"method": "POST",
"query": {},
"uri": "/api/v/4/webhook/execute/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx/findDevicesInStateWebhook/states/TX/devices/tractor",
"urlParams": {
"stateCode": "TX",
"deviceType": "tractor"
}
},
"service_instance_id": "cba54088-63a8-417c-ad2c-f8d02ec2eabf",
"systemKey": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"userEmail": "anon",
"userToken": "...",
"userid": "anon"
}